Optimization of vegetarian burger patties through mushroom substitution with peanut: Formulation, nutritional Profile, bioactivity, and consumer acceptability evaluation
Main Article Content
Abstract
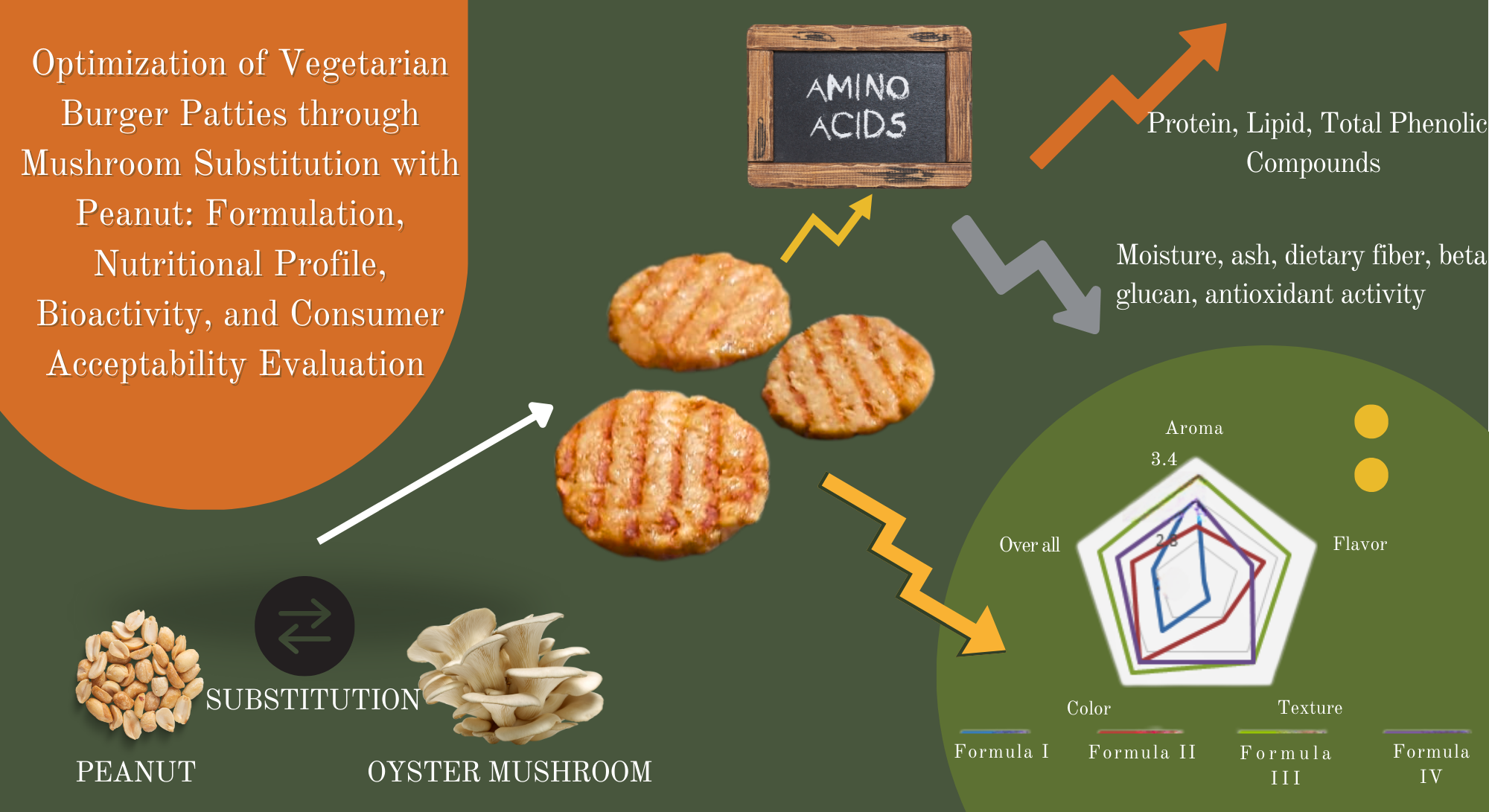
The consumption of meat has been linked to an increasing prevalence of various diseases and negative environmental impacts, highlighting the necessity for alternative protein sources. Oyster mushrooms (Pleurotus ostreatus) and peanuts (Arachis hypogaea) offer promising alternatives for use in vegetarian burger patties. Achieving the optimal ratio between oyster mushrooms and peanuts is crucial to produce a vegetarian burger that meets the desired standards of consumer acceptability, nutritional value, and bioactivity. Four different formulations of vegetarian burgers were developed, each varying in the level of mushroom-peanut substitution (0%, 5%, 10%, and 15%). Each formula was evaluated based on its nutritional value (moisture, ash, protein, fat, carbohydrate, and dietary fiber), bioactive compounds (antioxidant activity, total phenolic compounds, and β-glucan), and sensory attributes (color, aroma, flavor, texture, and overall acceptability). The selected formula was characterized for its amino acid profile. The results revealed that substituting mushrooms with peanuts led to an increase in protein content, lipid content, and total phenolic compounds, significantly impacting consumer acceptance in all vegetarian burger patty attributes. On the contrary, the addition of peanuts resulted in a reduction in moisture content, ash content, dietary fiber content, antioxidant activity, and β-glucan content. Meanwhile, it did not significantly impact consumer acceptance in all vegetarian burger patty attributes. After a thorough assessment, the formulation featuring a 10% peanut substitution was identified as the most optimal, striking a balance between sensory evaluation, nutritional value, and bioactivity of the vegetarian burger patty. Afterward, the selected formula was characterized for its free amino acids profile.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
González N, Marquès M, Nadal M, Domingo JL. Meat consumption: Which are the current global risks? A review of recent (2010–2020) evidences. Food Res Int. 2020;137:109341.
Arwanto V, Buschle-Diller G, Mukti YP, Dewi ADR, Mumpuni C, Purwanto MGM, et al. The state of plant-based food development and its prospects in the Indonesia market. Heliyon. 2022;8(10):e11062.
Yuliarti O, Ng L, Koh WM, Abdullah Tan MFBMF, Dwi Sentana A. Structural properties of meat analogue with added konjac gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2023;142:108716.
Samard S, Maung TT, Gu BY, Kim MH, Ryu GH. Influences of extrusion parameters on physicochemical properties of textured vegetable proteins and its meatless burger patty. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2021;30(3):395–403.
Echeverria-Jaramillo E, Shin WS. Black soybean cooking water (aquasoya) powder as a novel clean-label ingredient in plant-based vegan patties. Int J Food Sci Technol. 2023;58(10):5121–5133.
Herawati H, Kamsiati E. Characteristics of vegetarian patties burgers made from tofu and tempeh. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. 2021;653(1):012103.
Wang M, Zhao R. A review on nutritional advantages of edible mushrooms and its industrialization development situation in protein meat analogues. J Futur Foods. 2023;3(1):1–7.
Sirimuangmoon C, Lee SM, Guinard JX, Miller AM. A study of using mushrooms as a plant-based alternative for a popular meat-based dish. Asia Pac J Sci Technol. 2016;21(2):156–167.
Imran M, Liyan Z. Production of plant-based meat: functionality, limitations and future prospects. Eur Food Res Technol. 2023;249(9):2189–213.
Chen Y, Lan D, Wang W, Zhang W, Wang Y. Quality characteristics of peanut protein-based patties produced with pre-emulsified olive oil as a fat replacer: Influence of acylglycerol type. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;252:126262.
Setyawan RH, Saskiawan I, Widhyastuti N, Kasirah. Formulation of Instant Complementary Feeding Powder Fortified with Tempe and Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus). J Biologi Indones. 2021;17(1):57–65.
Elfirta RR, Ferdian PR, Saskiawan I, Handayani TH, Mandalika KFG, Riffiani R, et al. Antioxidant Properties of Kombucha Beverage Infused with Ganoderma lucidum and Green Tea from Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze with Several Fermentation Times. Karbala Int J Mod Sci.. 2024;10(1):141–152.
Singh A, Raina SN, Sharma M, Chaudhary M, Sharma S, Rajpal VR, et al. Functional uses of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) seed storage proteins. In: Jimenez-Lopez JC, editor. Grain and Seed Proteins Functionality. IntechOpen; 2021. p. 121–142.
Zhang G, Peng H, Zhang J, Wang S, Qi M, Zhishang R, et al. The effect of high-moisture extrusion on the water holding capacity of pea protein texturized products. IOSR J Agric Vet Sci. 2021;14(3):50–54.
Swing JS, Thompson TW, Guimaraes O, Geornaras ifigenia, Engle TE, Belk KE, et al. Nutritional composition of novel plant-based meat alternatives and traditional animal-based meats. Food Sci Nutr. 2021;7(3):1–12.
Cerletti C, Esposito S, Iacoviello L. Edible mushrooms and beta-glucans: Impact on human health. Nutrients. 2021;13(7):2195.
Setyawan RH, Iwan Saskiawan I, Widhyastuti N, Kasirah, Mulyadi. Prebiotic potency from White Oyster Mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) Extract. Ber Biologi. 2023;22(1):51-59.
Kaur R, Sharma M, Ji D, Xu M, Agyei D. Structural features, modification, and functionalities of beta-glucan. Fibers. 2020;8(1):1-29.
Abdullah FAA, Dordevic D, Kabourkova E, Zemancová J, Ali F, Abdullah A, et al. Antioxidant and sensorial properties: Meat analogues versus conventional meat products. Processes. 2022;10(9):1864.
Chu M, Khan RD, Zhou Y, Agar OT, Barrow CJ, Dunshea FR, et al. LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS characterization of phenolic compounds in common commercial mushrooms and their potential antioxidant activities. Processes. 2023;11(6):1711.
Win MM, Abdul-Hamid A, Baharin BS, Anwar F, Sabu MC, Pak-Dek MS. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of peanut’s skin, hull, raw kernel and roasted kernel flour. Pak J Bot. 2011;43(3):1635–1642.
Issaoui M, Delgado AM, Caruso G, Micali M, Barbera M, Atrous H, et al. Phenols, flavors, and the mediterranean diet. J AOAC Int. 2020;103(4):915–924.
Ray S. Sensory properties of foods and their measurement methods. In: Techniques to Measure Food Safety and Quality: Microbial, Chemical, and Sensory. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2021. p. 345–381.
Somdee T, Somdee T, Yangyuen S, Mungvongsa A, Kongphapa J. Amino acid composition and biological activity of new powdered vegetable seasonings. Asia Pac J Sci Technol. 2023;28(5):1–8.
Shu K, Ririka S, Kenji K, Manabu U, Osamu N. Key Aroma Compounds in Roasted In-shell Peanuts. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2013;77(7):1467–1473.
Patinho I, Selani MM, Saldaña E, Bortoluzzi ACT, Rios-Mera JD, da Silva CM, et al. Agaricus bisporus mushroom as partial fat replacer improves the sensory quality maintaining the instrumental characteristics of beef burger. Meat Sci. 2021;172:108307.
Flory J, Xiao R, Li Y, Dogan H, Talavera MJ, Alavi S. Understanding protein functionality and its impact on quality of plant-based meat analogues. Foods. 2023;12(17):3232.
Hou Y, Wu G. Nutritionally Essential Amino Acids. Adv Nutr. 2018;9(6):849-851.
Schaafsma G. The protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS)-A concept for describing protein quality in foods and food ingredients: A critical review. J AOAC Int. 2005;88(3):988–994.
Auclair O, Eustachio Colombo P, Milner J, Burgos SA. Partial substitutions of animal with plant protein foods in Canadian diets have synergies and trade-offs among nutrition, health and climate outcomes. Nat Food. 2024;5(2):148–157.