Novelty Seeking Affecting Intention Recommend of Tourists Visit to Banhunlek in Ang Thong Province: The Mediator Role of Tourists Experience
Main Article Content
Abstract
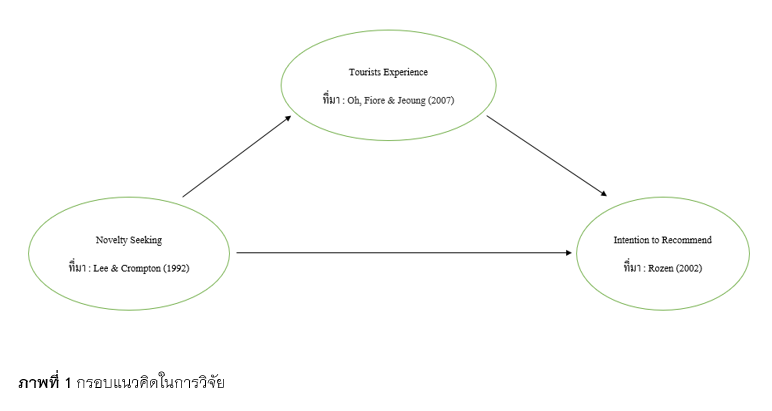
The research objectives were: 1) to study the level of novelty seeking, tourists experience and intention to recommend; 2) to study the effect of novelty seeking on intention to recommend; 3) to analyze tourists experience as a mediator between novelty seeking and intention to recommend. This study employed quantitative research methods, and questionnaires were used to collect data from 300 Thai tourists who had visited Banhunlek. Descriptive statistics, such as percentage, mean, standard deviation, skewness, kurtosis as well as inferential statistics (Path Analysis), were used to analyze the data. The Structural Equation Model (SEM) was used to determine which dimensions affected intention to recommend.
The results revealed that the level of novelty seeking and tourists experience was high, while intention to recommend was moderate. Additionally, 4 hypotheses were supported. The model was consistent with empirical data: chi-square test of goodness of fit = 31.573, relative chi-square = 1.503, p = .065, RESEA = .041, RMR = .013, GFI = .979, AGFI = .944, NFI = .994, TLI = .996. The variables in the model accounted for 78.9 % of the variance intention to recommend.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The articles published are copyrighted by the Graduate School, Chiang Mai Rajabhat University.
The opinions expressed in each article of this academic journal are solely those of the individual authors and do not reflect the views of Chiang Mai Rajabhat University or its faculty members. The responsibility for the content of each article rests entirely with the respective authors. In the event of any errors, the authors alone are responsible for their own articles.
References
Baron, R. M. & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological
research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal or Personality and Social Psychology, 51(6), 1173-1182.
Bui, V. T., Nuyen, Q. N. & Nguyen, T. T. T. (2020). Destination attractiveness impact novelty-motivation and satisfaction of tourists with ecotourism in an Binh Islet, Vinh Long Province. International Journal of Research and Review, 7(12), 438-441.
Buttri, P. (2020). "Baan Hun Lek", Ang Thong province is famous as far as foreign countries, After the famous Chinese media published the most creative work cool Thai people. Retrieved from https://mgronline.com/travel/detail/9630000066409 [In Thai]
Chanaumchokcharoen, F. (2020). Influence of experiential marketing towards satisfaction through intention to recommend and revisit of Thai tourists in Museum Siam. (Master’s thesis, Master of business administration, Silpakorn University). [In Thai]
Chill Pai Nai. (2021). 10 Check-in points, Eat, Travel, Ang Thong secondary provinces that are too beautiful to resist. Retrieved from https://www.chillpainai.com/scoop/13796 [In Thai]
Cohen, E. (1979). A phenomenology of tourist experiences. British Sociological Association, 13(12), 179-201.
Dayour, F. & Adongo, C. A. (2015). Why they go there: International tourists' motivations and revisit intention to Northern Ghana. American Journal of Tourism Management, 4(1), 7-17.
Douglas, A. J. & Vavra, D. (1995). Consumer behavior and marketing action. (5th ed.). Ohio: South-Western College Pub.
Eny, E. P. (2020). Novelty Seeking to predict behavior intention in rutal destination. Jurnal Bisnis Dan Manajemen, 7(2), 61-73.
Goo, J., Huang, C.D., Yoo, C.W. & Koo, C. (2022). Smart tourism technologies’ ambidexterity: BalancingTourist’s worries and novelty seeking for travel satisfaction. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-021-10233-6
Hair, Jr. J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J. & Anderson, R. E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Hair, J. F., Risher, J. J., Saratedt, M. & Ringle, C. M. (2019). When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. European Business Review, 31(1), 2-24.
Kline, R.B. (2005). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. (2nd ed.). New York: The Guilford Press.
Laowattanachai, P. (2019). The effect of destination image on behavior intention through memorable tourismexperience. (Master’s thesis, Master of business administration., Silpakorn University). [In Thai]
Larsen, S. (2007). Aspects of a psychology of the tourist experience. Scandinavian Journal of Hospitality and Tourism, 7(1), 7-18.
Lee, T. H. & Crompton, J. (1992). Measuring novelty seeking in tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 19(4), 732-751.
Likert, R. (1967). The method of constructing and attitude scale: Attitude theory and measurement. Fishbeic, Martin, Ed. New York: Wiley & Son.
Mitas, O. & Bastiaansen, M. (2018). Novelty: A mechanism of tourists’ enjoyment. Annals of Tourism Research, 7(2), 98-108.
Moon, H., & Han, H. (2019). Tourist experience quality and loyalty to an island destination: The moderating impact of destination image. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 36(1), 43-59.
Oh, H., Fiore, A.M. & Jeoung, M. (2007). Measuring experience economy concepts: Tourism applications. Journal of Travel Research, 46(2), 119-132.
Quoc, N. N., Huynh, L. N. & Thi, D. H. L. (2020). Relationships among novelty seeking, satisfaction, return intention, and willingness to recommend of foreign tourists in Vietnam. Growing Science, 10(10), 2249-2258.
Rasoolimanesh, S. M., Seyfi, S., Hall, C. M. & Hatamifar, P. (2021). Understanding memorable tourism experiences and behavioural intentions of heritage tourists. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 21(21), 100621.
Rozen, E. (2002). The anatomy of buzz: How to create word-of-mouth marketing. (2nd ed.). New York: Dubleday.
Samanrat, N. (2019). Tourism promotion for active aging tourist with perceived sense of terra incognita in Thailand. (Doctoral dissertation, Tourism management, Naresuan University). [In Thai]
Schumacker, R. E. & Lomax, R. G. (2016). A beginner’s guide to structural equation modeling. (4th ed.). New York: Routledge.
Schiffman, L. G. & Kanuk, L. L. (2007). Consumer behavior. (9th ed.). Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Sekaran, U. (1992). Research methods for business – A skill building approach. (2nd ed.). United States of America: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Sellick, M. C. (2004). Discovery, connection, nostalgia. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 17(1), 55-71.
Silverman, S. (2001). Essentials of oral medicine. Hamilton, London: BC Decker Inc.
Solomon, M. R. (2011). Consumer behavior: Buying, having, and being. (9th ed.). Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Thoo, P. Y., Johari, S., Ismail, M. H., & Yee, L. L. (2019). Understanding the role of memorable tourism experiences in loyalty at giant panda conservation centre, Zoo Negara Malaysia. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering, 7(5), 63-68.
Tourism Authority of Thailand. (2022). Performance according to 2022 annual action plan in foreign markets domestic market and organizational management for the first quarter 2022. Retrieved from https://www.tat.or.th [In Thai]
TTB Analytics. (2022). TTB analytics looks at travel in Thailand, the number of tourists in the second half of the year is expected to grow 161.7%. Retrieved from https://www.ttbbank.com/th/newsroom/detail/halfyear-travel-2565 [In Thai]
Westfall, P. H. & Henning, K. S. S. (2013). Understanding advanced statistical methods. Chapman & Hall/CRC Texts in Statistical Science Series. New York: Boca Raton.
Yuan, K. H., Wu, R & Bentler, P. M. (2011). Ridge structural equation modelling with correlation matrices for ordinal and continuous data. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 64(1), 107-133.