Problems and Factors Affecting English Listening and Speaking of Undergraduate Students, Chiang Mai Rajabhat University
Main Article Content
Abstract
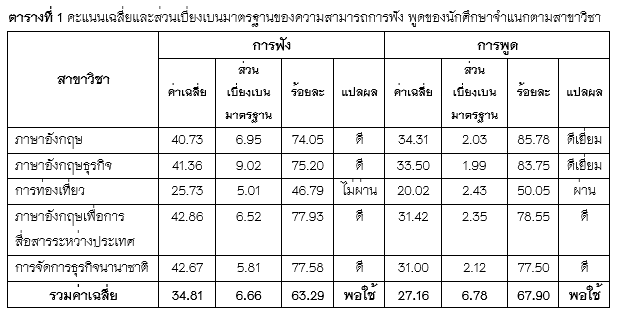
This study aimed at investigating 1) English listening and speaking proficiency levels 2) problems in listening and speaking English and 3) factors affecting English listening and speaking skills of undergraduate students at Chiang Mai Rajabhat University. A sample of 308 fourth-year undergraduate students using English for communication during their internship were purposively selected. The research instruments were a listening test, a speaking test, a questionnaire about factors affecting their listening and speaking, and a semi-structured interview. Data collected from the listening test and the speaking test was analyzed by percentage, mean, and standard deviation. Data collected from the questionnaires was analyzed by frequency, percentage, mean, standard deviation, and Multiple Regression Analysis. Data collected from the interview was analyzed through Coding Process. The results showed that 1) the students’ listening proficiency level was at the moderate level (= 34.81, S.D. = 6.66), similar to their speaking proficiency level (
= 27.16, S.D. = 6.78); 2) the students did not have problems in listening when considered by purposes of listening, nor problems in speaking when considered by elements of speaking; and 3) the factors affecting their listening at 0.05 level of significant were input factor, speaker and listening text factor, and teaching and learning factor, while the factors affecting their speaking at 0.05 level of significant were learner factor, and teaching and learning factor.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The articles published are copyrighted by the Graduate School, Chiang Mai Rajabhat University.
The opinions expressed in each article of this academic journal are solely those of the individual authors and do not reflect the views of Chiang Mai Rajabhat University or its faculty members. The responsibility for the content of each article rests entirely with the respective authors. In the event of any errors, the authors alone are responsible for their own articles.
References
กระทรวงศึกษาธิการ. (2561). รายงานการศึกษาไทย พ.ศ. 2561. กรุงเทพฯ: พริกหวานกราฟฟิค. สืบค้นจาก https://pmnk.kkzone1.go.th/data/news3/24-02-2019-17-34-35_1344028011.pdf
จุไรรัตน์ สวัสดิ์, เสน่ห์ สวัสดิ์, และ วจี พวงมณี. (2560). ศึกษาปัญหาการสื่อสารภาษาอังกฤษกับอาจารย์ชาวต่างประเทศของนักศึกษา สาขาวิชาภาษาอังกฤษเพื่อการสื่อสารสากล มหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีราชมงคลล้านนา น่าน. ใน การประชุมวิชาการมหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีราชมงคล ครั้งที่ 9 "ราชมงคลสร้างสรรค์นวัตกรรมที่ยั่งยืนสู่ประเทศไทย 4.0" (น. 303-311). 10 สิงหาคม 2560. นนทบุรี: ศูนย์แสดงสินค้าและการประชุม อิมแพ็ค เมืองทองธานี, สาขามนุษยศาสตร์สังคมวิทยาและการศึกษา มหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีราชมงคลล้านนา น่าน.
ณัฏฐ์นรี ฤทธิรัตน์. (2556). ความสามารถด้านการพูดภาษาอังกฤษและปัญหาในการพัฒนาทักษะ การพูดภาษาอังกฤษของนักศึกษามหาวิทยาลัยไทย. (วิทยานิพนธ์ศิลปศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต, สาขาวิชาการสอนภาษาอังกฤษเป็นภาษานานาชาติ มหาวิทยาลัยสงขลานครินทร์).
นงสมร พงษ์พาณิช. (2554). การศึกษาปัญหาการพูดภาษาอังกฤษในการสื่อสารด้วยวาจาของนิสิตคณะวิทยาการจัดการ มหาวิทยาลัยเกษตรศาสตร์ วิทยาเขตศรีราชา ตุลาคม 2550 ถึง กันยายน 2551. วารสารมนุษยศาสตร์, 18(1), 85-97.
วอยซ์ออนไลน์. (2564). ความสามารถภาษาอังกฤษคนไทยรั้งท้ายโลก-ต่ำสุดในอาเซียน. สืบค้นจาก https://voicetv.co.th/read/RoOK3kU5F
Ali, Y. (2020). Difficulties faced by tertiary level EFL learners in listening. British Journal of English Linguistics, 8(2), 90-112.
Anderson, A., & Lynch, T. (1998). Listening. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Bozorgian, H. (2012). The relationship between listening and other language skills in international language testing system. Theory and Practice in Language Studies, 2(4), 657-663.
Celik, O., & Yavuz, F. (2015, February). The relationship between speaking grades and listening grades of university level preparatory students. Prodedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 197, 2137-2140.
Chen, A. (2013). EFL listeners’ strategy development and listening problems: A process-based study. The Journal of Asia TEFL, 10(3), 81-101.
Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika, 16, 297–334.
Cubalit, A. (2016). Listening comprehension problems of Thai university English learners. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Language, Literature & Society (207-214), (n.d.). Sri Lanka: International Center for Research and Development.
Demir, S. (2017). An evaluation of oral language: The relationship between listening, speaking and self-efficacy. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 5(9), 1457-1467.
Doromae, A. (2018). The problem faced by Thai students in speaking English skill at University of Muhammadiyah Malang. (Undergraduate of Education thesis, English Language Education, University of Muhammadiyah Malang).
Educational Testing Service. (2012). TOEIC examinee handbook speaking & writing. Retrieved from http://www.toeic.com.sg/wp-content/files/TOEIC_Speaking_ and_Writing_Examinee_Handbook.pdf
Education First. (2021). EF English proficiency index: A ranking of 112 countries and regions by English skills. Retrieved from https://www.ef.com/assetscdn/ WIBIwq6RdJvcD9bc8RMd/cefcom-epi-site/reports/
/ef-epi-2021-english.pdf
Heriansyah, H. (2012). Speaking problems faced by the English department students of Syiah Kuala University. Lingua Didaktika Jurnal Bahasa dan Pembelajaran Bahasa, 6(1), 37-44.
Hossain, M. I. (2015). Teaching productive skills to the students: A secondary level scenario. (Master of Arts thesis, English, BRAC University).
Hu, L. (2007). Long pauses in Chinese EFL learners’ speech production. Interlinguistica, 17, 606-616.
Juhana, J. (2012). Psychological factors that hinder students from speaking in English class (A case study in a senior high school in south Tangerang, Banten, Indonesia). Journal of Education and Practice, 3(12), 100-110.
Khamprated, N. (2012). The problems with the English listening and speaking of students at a private vocational school in Bangkok. (Master of Arts project, Teaching English as a Foreign Language, Srinakharinwirot University).
Koran, S. (2015). The role of teachers in developing learners' speaking skill. In Proceedings of the 6th International Visible Conference on Educational Studies and Applied Linguistics 400-416.
Kuder, G. F., & Richardson, M. W. (1937). The theory of the estimation of test reliability. Psychometrika, 2, 151–160. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02288391
Leong, L.-M., & Ahmadi, S. M. (2017). An analysis of factors influencing learners’ English speaking skill. International Journal of Research in English Education, 2(1), 34-41.
Nan, C. (2018). Implications of interrelationship among four language skills for high school English teaching. Journal of Language Teaching and Research, 9(2), 418-423.
Naipinit, A., Kroeksakul, P., & Promsaka Na Sakolnakorn, T. (2014). Adjustment under globalization. SKRU Academic Journal, 7(1), 1-12.
Sadiku, L. M. (2015). The importance of four skills in reading, speaking, writing, listening in a lesson hour. European Journal of Language and Literature Studies, 1(1), 29-31.
Strauss, A., & Corbin, J. (1990). Basics of qualitative research: Grounded theory procedures and techniques. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Suwannasit, W. (2019). EFL learners’ listening problems, principles of teaching listening and implications for listening instruction. Journal of Education Naresuan University, 21(1), 345-359.
Tran, T. Q., & Duong, T. M. (2020). Insights into listening comprehension problems: A case study in Vietnam. PASAA, 59, 77-100.
Tuan, N. H., & Mai, T. N. (2015). Factors affecting students’ speaking performance at Le Thanh Hien High School. Asian Journal of Educational Research, 3(2), 8-23.
Wattajarukiat, T., Chatupote, M., & Sukseemuang, P. (2012). An investigation of English listening strategies used by Thai undergraduate students in public universities in the south. Journal of Liberal Arts Prince of Songkla University, 4(2), 1-17.
Yamane, T. (1973) Statistics: An introductory analysis. (3rd ed.) New York: Harper and Row.