Analysis of Challenges and Factors Affecting Critical Reading Abilities of English Major Students
Main Article Content
Abstract
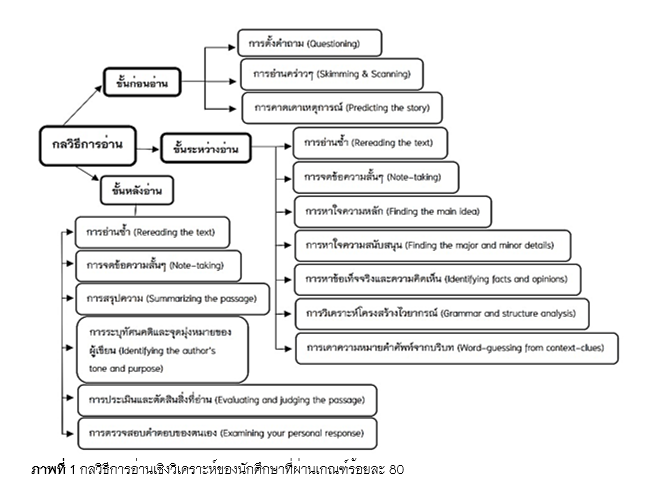
The purposes of this research were to investigate the challenges pertaining to the critical reading abilities of English major students, the factors affecting these students’ critical reading abilities, and approaches to enhance their critical reading abilities. The sample group in this study consisted of 125 English major students in their 3rd and 4th years. Purposive sampling and volunteer sampling techniques were applied to select the participants of this study. The research instruments consisted of a critical reading test, a questionnaire, and an interview. The quantitative data were then analyzed by percentage, mean, standard deviation, correlation coefficient, and multiple regression analysis. The results revealed that the students’ critical reading abilities were at a low level (59.13%). Among the five major areas of critical reading abilities, the students scored the lowest in “Evaluating and judging the context” and “Making inferences”. Besides, the factors affecting the students’ critical reading abilities, at a .05 significance level appeared to have been reading techniques and motivation. As a result, the effective approaches to nurture the students’ critical reading abilities should incorporate reading techniques, promote a growth mindset, and consider the role of the instructors as well as motivation and the students’ attitudes.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The articles published are copyrighted by the Graduate School, Chiang Mai Rajabhat University.
The opinions expressed in each article of this academic journal are solely those of the individual authors and do not reflect the views of Chiang Mai Rajabhat University or its faculty members. The responsibility for the content of each article rests entirely with the respective authors. In the event of any errors, the authors alone are responsible for their own articles.
References
Adams, W. R. & Patterson, B. (2005). Developing reading versatility. Boston: Wadsworth.
Bachelor of Arts. (2021). A report of employer satisfaction towards graduates in Bachelor of Arts Program in English, academic year 2021. Chiang Mai: Chiang Mai Rajabhat University. [In Thai]
Bachelor of Arts. (2022). A report of organization satisfaction towards student trainees’ communication skills in Bachelor of Arts Program in English, academic year 2022. Chiang Mai: Chiang Mai Rajabhat University. [In Thai]
Banditvilai, C. (2020). The effectiveness of reading strategies on reading comprehension. International Journal of Social Science and Humanity, 10(2), 46 – 50.
Bharuthram, S. (2012). Making a case for the teaching of reading across the curriculum in higher education. South African Journal of Education, 32(2), 205-214.
Blackwell, L. A., Trzesniewski, K. H., & Dweck, C. S. (2007). Theories of intelligence and achievement across the junior high school transition: A longitudinal study and an intervention. Child Development, 78(1), 246-263.
Chiang Mai Rajabhat University. (2019). Announcement of the university on the policy to raise the standard of English language of Chiang Mai Rajabhat students in 2019. Retrieved from http://www.general.cmru.ac.th/infocenter/condec/ConCmdFiles/2562/08 82562.pdf [In Thai]
Caine, R. N., Caine, G., McClintic, C. M., & Klimek, K. J. (2009). 12 brain and mind learning principles in action: Developing executive function brain of human. (2nd ed.). California: Corwin Press.
Conklin, W. (2012). Higher-order thinking skills to develop 21st century learners. California: Shell Education.
Duangloi, M. (2015). Factors affecting English reading problems of students in Rajamangala University of Technology Krungthep. Journal of Technical Education Rajamangala University of Technology Thanyaburi, 3(1), 151-165. [In Thai]
Dweck, C. S. (2006). Mindset: The new psychology of success. New York: Random House.
Dwiastuty, N. & Nurjanah, N. (2018). Reading skills test through Bloom’s taxonomy. Deiksis Journal, 8(3), 279-287.
Education First. (2022). EF English proficiency index: A ranking of 111 countries and regions by English skills. Retrieved from https://www.ef.com/assetscdn/WIBIwq6RdJvcD9bc8RMd/cefcom-epi-site/reports/2022/ef-epi-2022-english.pdf
Gardner, R. C. (2002). Integrative motivation and second language acquisition. In Dörnyei, Z., & Schmidt, R. W. (Eds.). Motivation and second language acquisition. (2nd ed.). Honolulu: National Foreign Language Resource Center.
Gardner, R. C. (2010). Motivation and second language acquisition: The socio-educational model. New York: Peter Lang Publishing.
Ghanea, M., Pisheh, H. R., & Ghanea, M. H. (2011). The relationship between learners-motivation (Integrative and Instrumental) and English proficiency among Iranian EFL learners. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, International Journal of Social, Behavioral, Educational, Economic, Business and Industrial Engineering, 5(11), 1368-1374.
Gilakjani, A. P. & Sabouri, N. B. (2016). A Study of factors affecting EFL learners’ reading comprehension skill and the strategies for improvement. International Journal of English Linguistics, 6(5), 180-187.
Gunning, T. G. (1992). Creating instruction for all children. England: A Division of Simon & Schuster.
Harris, L. A., & Smith, C. B. (1986). Reading instruction: Diagnostic teaching in the classroom. (3rd ed.). New York: Mc Graw-Hill.
Hong-Nam, K. & Leavell, A. G. (2006). Language learning strategies of EFL students in an intensive English learning context. System, 3(4), 399-415.
Jianfeng, Z. (2014). A study of senior students’ critical reading competence via analyzing their reading reports. Teaching and Educational Research, 8(1), 215-221.
Kelly, M. (2020). Bloom’s taxonomy questions: Question stems to help apply Bloom’s taxonomy. Retrieved from https://www.thoughtco.com/blooms-taxonomy-questions-7598
Khazanie, R. (1996). Statistics in a world of applications. (4th ed.). New York: Harper Collins College Publishers.
Krathwohl, D. R. (2002). A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy: An overview. Theory into Practice, 41(4), 212-218.
Kucer, S. B. (2016). Accuracy, miscues, and the comprehension of complex literary and scientific texts. Reading Psychology, 37(7), 1076–1095.
Küçükoğlu, H. (2012). Improving reading skills through effective reading strategies. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 70, 709-714. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.01.113
Mather, P. & McCarthy, R. (1999). The art of critical reading. Boston: Heinle & Heinle.
Ministry of Education. (2018). Education in Thailand 2018. Retrieved from http://pmnk.kkzone1.go.th/data/news3/24-02-2019-17-34-35_1344028011.pdf [In Thai]
Narkprom, N., Phusiripinyo, W., & Saito, S. (2016). A survey study of English reading problems of the 4th year students in English Education, Phetchabun Rajabhat University. In the 16th national northern Rajabhat graduate research conference and the 3rd Phetchabun Rajabhat University conference, (pp. 176-185). 12 December 2017. Phetchabun: Research and Development Institute, Phetchabun Rajabhat University. [In Thai]
Neamnoy, A. (2008). Improve critical reading through SQ3R method. Bangkok: Suweerivasarn. [In Thai]
Office of the Basic Education Commission. (2015). The common European framework of reference for languages. Retrieved from http://English.obec.go.th/englush/2013/index.php/th/2012-08-08-10-26-5/74-cefr [In Thai]
Raphael, T. E., George, M., Weber, C. M., & Nies, A. (2009). Approaches to teaching reading comprehension. In Handbook of research on reading comprehension. New Jersey: Routledge Taylor & Francis Group.
Richek, M. A., Caldwell, J. S., Jennings, J. H., & Lerner, J. W. (1996). Reading problems: Assessment and teaching strategies. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Rohmah, G. N. (2018). Critical reading: Students’ problems, strategies, and reflections. Journal of English Language and Teaching, 2(1), 21-26.
Sereidi, M. A., Sheikh, N. A., & Takriti, R. (2019). Critical reading experiences by Emirati 11th grade students with regard to Bloom’s Taxonomy. Journal of Applied Linguistics and Language Research, 6(6), 16-29.
Strauss, A. & Corbin, J. (1990). Basics of qualitative research: Grounded theory procedures and techniques. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Van Den Broek, P. & Espin, C. A. (2012). Connecting cognitive theory and assessment: Measuring individual differences in reading comprehension. School Psychology Review, 41(3), 315–325.
Wimolmas, R. (2013). A survey study of motivation in English language learning of first year undergraduate students at Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology (SIIT), Thammasat University. FLLT Conference Proceedings by LITU, 2(1), 904-915.
Yang, Y. F. (2002). Reassessing readers’ comprehension monitoring. Reading in a Foreign Language, 14(1), 18-42.
Yu, B. & Downing, K. (2012). Determinants of international students’ adaptation: Examining effects of integrative motivation, instrumental motivation and second language proficiency. Educational Studies, 38(4), 457-471. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1080/03055698.2011.643111
Yu, J. (2015). Analysis of critical reading strategies and its effect on college English reading. Theory and Practice in Language Studies, 5(1), 134-138.