Community Participation in Justice Management to Prevent and Solve Recidivism Problems of Ex-Convicts: A Case Study of Upper Southern Provinces
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14456/psruhss.2024.4Keywords:
Participation, Recidivism, Ex-convicts, Upper Southern ProvincesAbstract
The study of community participation in justice management to prevent and solve recidivism problems of ex-convicts: a case study of upper southern provinces aimed to 1) study and analyze problems about the recidivism of the ex-convicts 2) study and analyze community participation appropriate for preventing recidivism, and 3) recommend the guidelines of community participation that is effective and appropriate for preventing recidivism of the ex-convicts. This study was qualitative research depending on in-depth interviews and focus groups from the key informants meanwhile research tools were the forms of in-depth interviews and focus groups. After the accuracy of the data was validated, it was then analyzed through content analysis. According to research findings, it was found that: 1) according to the problem of recidivism of the ex-convicts and the obstacles of the community in preventing recidivism in the areas of upper southern provinces of Thailand, it was indicated that the upper southern provinces with the highest recidivism are Nakhon Si Thammarat with 200 offenders, Surat Thani with 134 offenders, Phuket with 104 offenders, and Furthermore, there were 587 ex-convicts who committed recidivism from the year 2015 to 2019, as for recidivism, there were 587 offenders caused by personal factors of the ex-convicts, such as mental problem, family and environment background (accommodation), feeling worthless, and unfavorable community condition forcing to a group of
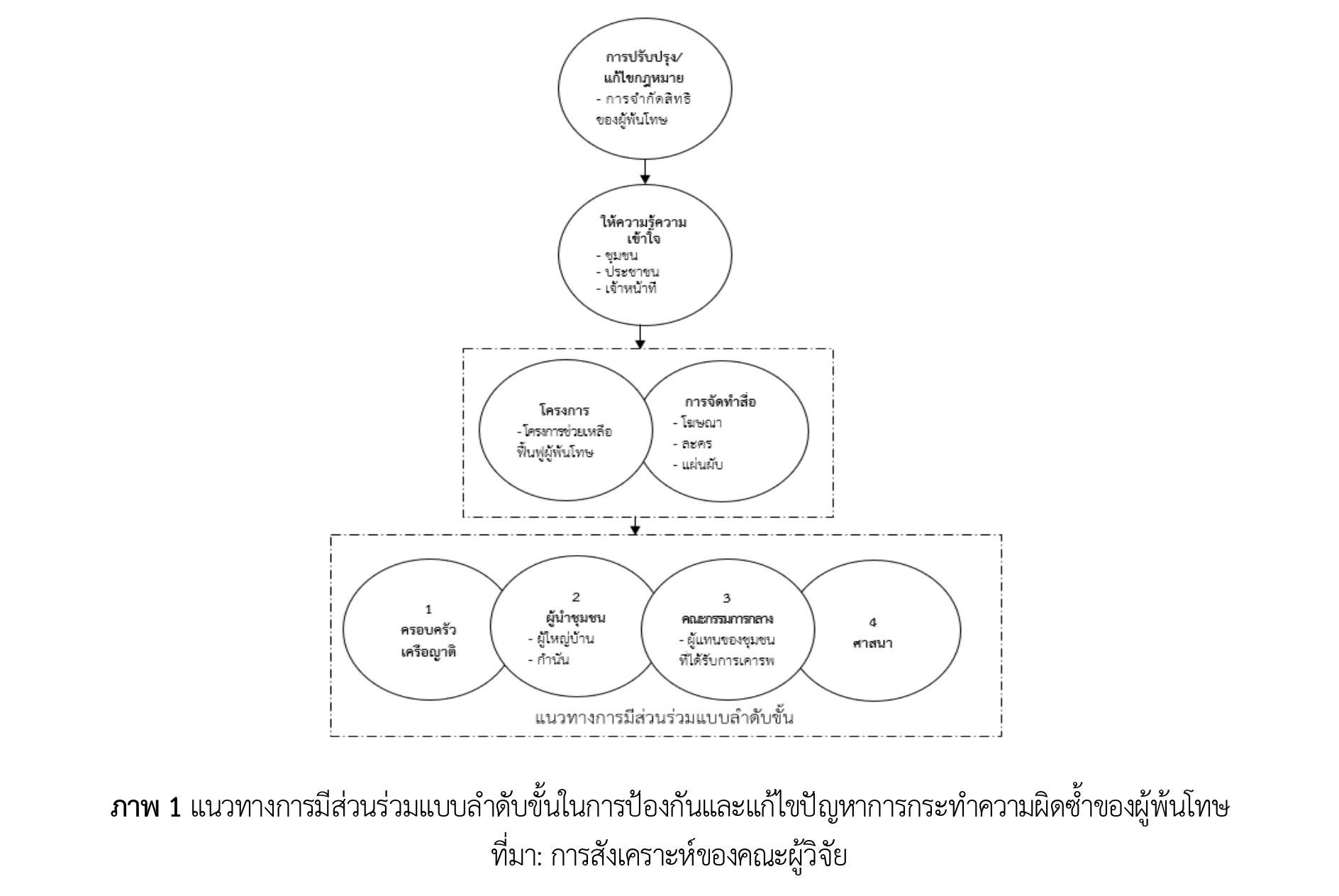
ex-convicts to become recidivists again, and also legal factors and justice procedures. The ex-convicts have no rights to make career since the law prescribes prohibited characteristics in occupation or works of those who used to be sentenced in imprisonment, such as Lawyers Act, B.E. 2528, Civil Service Act, B.E. 2551, Health Business Establishments Act, B.E. 2559, Section 13, and other 25 acts that restrict the rights of those sentenced convicts, 2) community participation appropriate for preventing recidivism indicated that that it is necessary to have the guidelines of community participation composing of adjusting the laws, building knowledge and understanding about the ex-convicts, making public relation media, initiating the projects, promoting family participation (relatives of the ex-convicts) using the middleman for mediation, setting the committee to nominate the senior representatives of community who were accepted from community, who were disciplined and passed religious principles, and 3) according to the guidelines in community participation that is effective and appropriate for preventing recidivism of the ex-convicts, since some areas or communities have different participation, the formats of community participation should be chosen to suit the context of community and locality in order to make it efficient in preventing and solving the problems of recidivism of the ex-convicts further and there are recommendations, especially in terms of the law. There should be amendments to the law that prescribes qualifications prohibiting inmates, occupation, or deleting the criminal record of the acquitted inmates within a set period of time failure to commit crimes within the specified time period is an opportunity for a better life. When these acquitted are able to make a living to earn money for themselves and not return to commit the same offense again, making society is safe because the acquitted have a career and do not want to go back to prison again.
References
กรมราชทัณฑ์. (2562). ฐานข้อมูลผู้ต้องขังกระทำความผิดซ้ำ. สืบค้น 19 มีนาคม 2562, จาก http://www.correct.go.th/recstats/
กรมราชทัณฑ์. (2562). อัตราการกระทำความผิดซ้ำแยกตามการค้นหาเฉพาะ. สืบค้น 15 มีนาคม 2563, จาก http://www.correct.go.th/recstats/index.php/th/searchAdvance
นิธิตา สิริพงศ์ทักษิณ. (2561). ยุติธรรมเชิงสมานฉันท์: การจัดการความขัดแย้งเพื่อสร้างความยุติธรรมของชุมชน
พรุควนเคร็ง จังหวัดนครศรีธรรมราช. วารสารพัฒนาสังคม, 20(1), 2-16.
นิมิต ทัพวนานต์. (2561). การพัฒนาแนวทางการป้องกันการกระทำความผิดซ้ำของผู้ต้องขังไร้ญาติ. กรุงเทพฯ: วิทยาลัยป้องกันราชอาณาจักร.
พงษ์กฤษณ์ มงคลสินธุ์. (2561). การศึกษาปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับการกระทำความผิดซ้ำในคดียาเสพติด. วารสารวิชาการแสงอีสาน, 15(1), 47-63.
พรชัย ขันตี. (2549). การบูรณาการทฤษฎีทางอาชญาวิทยา การบริหารงานยุติธรรมและสังคม (2557101). เอกสารประกอบการบรรยาย (ปรัชญาดุษฎีบัณฑิต). กรุงเทพฯ: มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏสวนดุสิต.
รุจิระ บุนนาค. (2560). ปัญหาเรือนจำ. สืบค้น 19 ตุลาคม 2562, จาก http://www.marutbunnag.com/article/494/
วีระชัย เหล่าลงอินทร์, เกรียงศักดิ์ ไพรวรรณ, สุวกิจ ศรีปัดถา, และพัชนี บูระพันธ์. (2552). การกระทำความผิดซ้ำของผู้ต้องขังในเรือนจำจังหวัดมหาสารคาม. วารสารมหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏมหาสารคาม; ว.มรม, 3(1), 29-38.
ศิลป์ชัย ลีลิตธรรม. (2563). การศึกษาปัจจัยและแนวทางป้องกันตามหลักเบญจศีลเพื่อส่งเสริมการไม่กระทำความผิดซ้ำ ของผู้ต้องขังในเรือนจำจังหวัดสมุทรปราการ. กรุงเทพฯ: มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏธนบุรี.
สำนักวิจัยและพัฒนาระบบงานราชทัณฑ์. (2549). แบบแผนการดำเนินชีวิตผู้ต้องขังกระทำความผิดซ้ำ: กรณีศึกษาพวกงัดแงะย่องเบา. กรุงเทพฯ: กรมราชทัณฑ์.
เสริมศรี ประสงค์สุข. (2546). พฤติกรรมการกระทำผิดและการปรับตัวของผู้ต้องขังชายที่มีพฤติกรรมเบี่ยงเบนทางเพศ ศึกษาเฉพาะกรณีเรือนจำและทัณฑสถานในเขตกรุงเทพมหานคร. กรุงเทพฯ: มหาวิทยาลัยธรรมศาสตร์.
อภิรดี พลีน้อย, บรรพต ต้นธีรวงศ์, และอดุลย์ ขันทอง. (2555). การพัฒนาการจัดการความขัดแย้งในชุมชนโดยใช้กระบวนการไกล่เกลี่ยข้อพิพาทชุมชนโดยอาสาสมัครไกล่เกลี่ยข้อพิพาทชุมชน. วารสารวไลยอลงกรณ์ปริทัศน์, 2(2), 39-48.
อัคคกร ไชยพงษ์. (2555). การพัฒนากลยุทธ์การป้องกันและแก้ไขปัญหาการกระทำความผิดซ้ำของผู้ต้องขังชายในเรือนจำเขต 8. วารสารมนุษยศาสตร์และสังคมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏสุราษฎร์ธานี, 4(1), 125-148.
อานนท์ ฉัตรเงิน, และเกษมศานต์ โชติชาครพันธุ์. (2559). ลักษณะส่วนบุคคลและพฤติกรรมของผู้กระทำความผิดซ้ำหญิงในคดีจำหน่ายยาเสพติด. วารสารวิชาการบัณฑิตวิทยาลัย มหาวิทยาลัยสวนดุสิต, 12(2), 71-86.
อุทัย ปริญญาสุทธินันท์. (2556). การจัดการความขัดแย้งเพื่อสร้างความยุติธรรมเชิงสมานฉันท์ของชุมชนควนโส. วารสารวิจัยสังคม, 36(2), 69-97.
De Claire, K., & Dixon, L. (2017). The Effects of Prison Visits From Family Members on Prisoners’ Well-Being, Prison Rule Breaking, and Recidivism: A Review of Research Since 1991. Trauma, Violence, & Abuse, 18(2), 185–199. https://doi.org/10.1177/1524838015603209
Mills, A. (2005). ‘Great expectations?’: A review of the role of prisoners’ families in England and Wales. In Selected Papers from the 2004 British criminology conference (Vol. 7, pp. 6-9). University of Portsmouth.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Humanities and Social Sciences Journal of Pibulsongkram Rajabhat University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Any articles or comments appearing in the Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, Rajabhat Phibulsongkram University, are the intellectual property of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect the views of the editorial board. Published articles are copyrighted by the Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, Rajabhat Phibulsongkram University.








