แบบสมรรถนะการทำงานแบบไฮบริดสำหรับบุคลากรมหาวิทยาลัยสายสนับสนุน Competency Model of Hybrid Working for Supporting Personnel of the University
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14456/psruhss.2024.50Keywords:
Competency, Hybrid working, Supporting personnel of the universityAbstract
The purposes of this research study in title of Competency model of hybrid working for supporting personnel of the university were as followed: (1) to study, analyze, and synthesize both abilities and competency components required for hybrid working among supporting personnel in a public university using the qualitative research approach. This was involved in review literature and focus group discussion with 26 supporting personnel members in a public university, working across four sectors according to the university missions including graduate production, research, academic service, and art and cultural preservation. The research discussion question tool was evaluated and revised by five experts in this field. Additionally, (2) to develop and validate a competency model of hybrid working for supporting personnel of the university. The evaluation and suggestions were used as the research tool. All data values were statistically analyzed and presented using the mean and standard deviation.
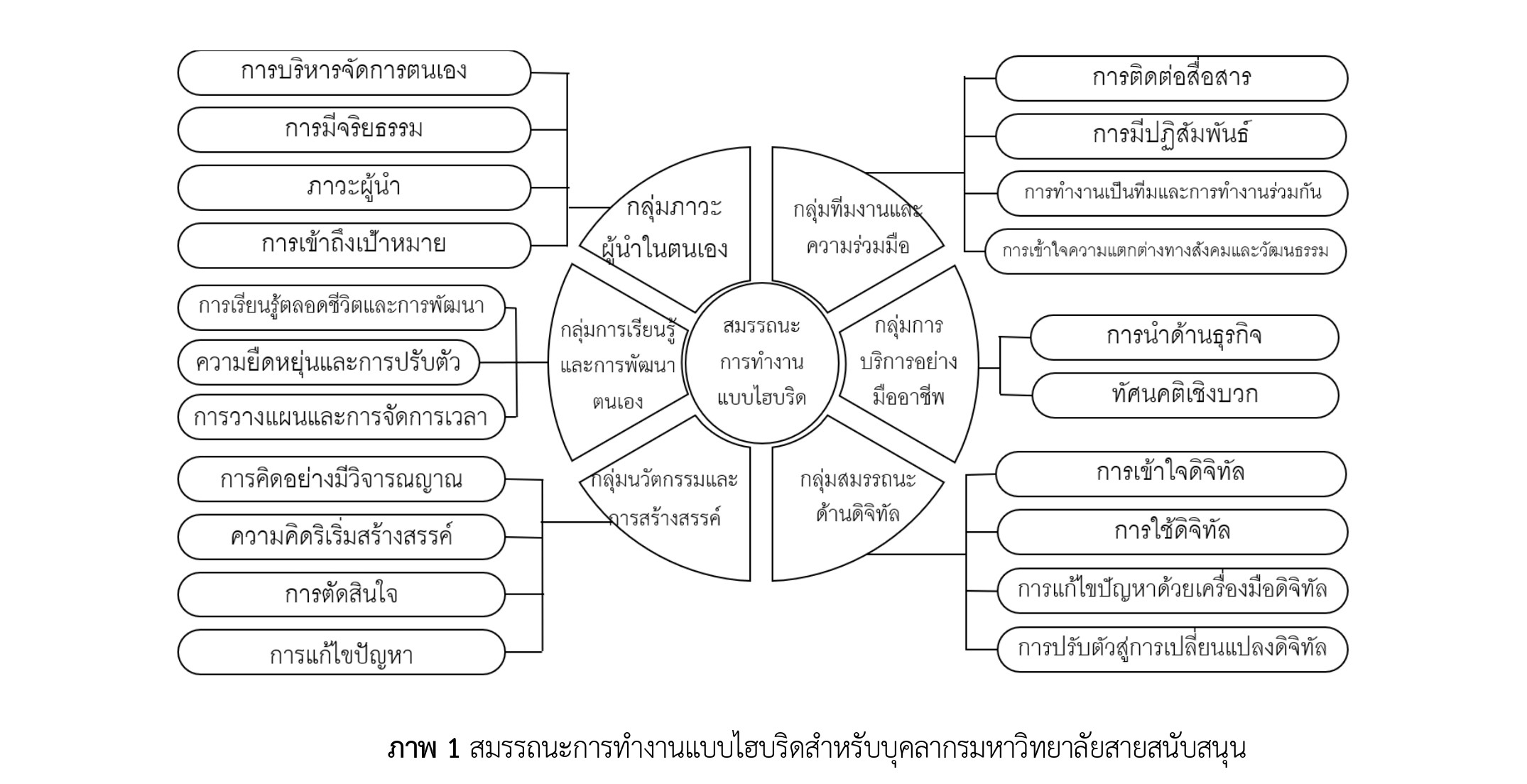
The competency model was developed with three main sections, including competency titles, competency definitions, and competency levels. It then submitted for evaluation by five academic specialists. The assessment results revealed a high level of appropriateness and possibility for a competency model of hybrid working for supporting personnel of the university ( = 4.40) (S.D.= 0.63). The six competency groups were classified as follows: (1) Self – Leadership, (2) Learning and Self – Development, (3) Innovation and Creativity, (4) Teamwork and Co-operation, (5) Professional service and (6) Digital competencies.
References
กรมการพัฒนาชุมชน. (2562). กถาพัฒนากร. สืบค้น 3 ธันวาคม 2567, จาก https://online.anyflip.com/mmler/mxpn/mobile/index.html
กฤษณพงศ์ กีรติกร, สันติ เจริญพรพัฒนา, วรรณา เต็มสิริพจน์, ศศิธร สุวรรณเทพ และชมพูนุท สวนกระต่าย. (2560). ประสิทธิภาพและการบริหารจัดการ ของมหาวิทยาลัยในกำกับของรัฐ (รายงานการวิจัย). กรุงเทพฯ: สำนักงานเลขาธิการสภาการศึกษา.
กล้าณรงค์ แสนพะเยาว์, ไอรดา โตเทศ และกัมปนาท วงษ์วัฒนพงษ์. (2565). ทักษะที่จําเป็นของคนทํางานภาครัฐในโลกอนาคต Skills Needed by Government Workers in The Future World. วารสารการบริหารและสังคมศาสตร์ปริทรรศน์, 5(3), 131-140.
ธนกฤต อั้งน้อย. (2562). รูปแบบการพัฒนาสมรรถนะครูใหม่ในศตวรรษที่ 21 ตามแนวคิดโรงเรียนเป็นองค์การแห่งการเรียนรู้. (วิทยานิพนธ์การศึกษาดุษฎีบัณฑิต). พิษณุโลก: มหาวิทยาลัยนเรศวร.
ปิยฉัตร คนชม. (2564). แบบสมรรถนะทางสังคมของนักเรียนโรงเรียนขยายโอกาส. (วิทยานิพนธ์การศึกษาดุษฎีบัณฑิต). พิษณุโลก: มหาวิทยาลัยนเรศวร.
ศูนย์วิจัยและสนับสนุนเป้าหมายการพัฒนาที่ยั่งยืน SDG MOVE มหาวิทยาลัยธรรมศาสตร์. (2565). ข้อมูลเบื้องต้นเกี่ยวกับ SDGs. สืบค้น 24 มีนาคม 2565, จาก https://www.sdgmove.com/intro-to-sdgs/
สมพร ปานดำ. (2563). พลิกวิกฤตสู่โอกาสของอาชีวศึกษาไทยบนความปกติใหม่. วารสารสังคมศาสตร์และมานุษยวิทยาเชิงพุทธ, 5(7), 1-13.
สหประชาชาติ ประเทศไทย. (2564). กรอบความร่วมมือว่าด้วยการพัฒนาที่ยั่งยืน วาระปี พ.ศ. 2565 - 2569. สืบค้น 23 พฤษภาคม 2566, จาก https://thailand.un.org/th/166885-krxbkhwamrwmmuuexwadwykarphathnathiiyangyuuen-warapii-phs-2565-2569
สำนักงานคณะกรรมการข้าราชการพลเรือน. (2563). คู่มือแนวทางการพัฒนาบุคลากรภาครัฐ พ.ศ. 2563 – 2565. สืบค้น 23 พฤษภาคม 2565, จาก https://www.ocsc.go.th/sites/default/files/attachment/page/guide_civilservice_update.pdf
สำนักงานคณะกรรมการดิจิทัลเพื่อเศรษฐกิจและสังคมแห่งชาติ. (2563). กรอบสมรรถนะด้านดิจิทัลสำหรับพลเมืองไทย. สืบค้น 24 ธันวาคม 2566, จาก https://www.onde.go.th/assets/portals/1/files/digital_competence_framework_for_thai_citizens.pdf
สำนักงานคณะกรรมการพัฒนาการเศรษฐกิจและสังคมแห่งชาติ. (2562). ยุทธศาสตร์ชาติระยะ 20 ปี (พ.ศ. 2561-2580) (พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 2). กรุงเทพฯ: สำนักงานเลขานุการของคณะกรรมการ ยุทธศาสตร์ชาติ สำนักงานคณะกรรมการพัฒนาการเศรษฐกิจและสังคมแห่งชาติ.
สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงการอุดมศึกษาวิทยาศาสตร์ วิจัยและนวัตกรรม. (2564). ข้อมูลสถิติบุคลากรในสถาบันอุดมศึกษา จำแนกตามตำแหน่งทางวิชาการ วิทยฐานะ และประเภทสถาบัน. สืบค้น
พฤศจิกายน 2566, จาก https://info.mhesi.go.th/homestat_stf.php
สำนักงานพัฒนารัฐบาลดิจิทัล. (2566). แผนพัฒนารัฐบาลดิจิทัลของประเทศไทย พ.ศ. 2566-2570. สืบค้น
มีนาคม 2567, จาก https://www.dga.or.th/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/DGA_2566-2570.pdf
สำนักงานสภาพัฒนาการเศรษฐกิจและสังคมแห่งชาติ. (2565). แผนพัฒนาเศรษฐกิจและสังคมแห่งชาติ ฉบับที่ 13
(พ.ศ. 2566-2570). สืบค้น 30 สิงหาคม 2565, จาก https://www.nesdc.go.th/article_attach/article_file_20230307173518.pdf
อนันต์ ทองชันลุก. (2563). การพัฒนาสมรรถนะการปฏิบัติงานของบุคลากร กลุ่มงานพัฒนาสมรรถนะวิชาชีพและตำแหน่ง สถาบันพัฒนาข้าราชการกรุงเทพมหานคร. รวมบทความวิจัย การศึกษาอิสระของนักศึกษาโครงการรัฐประศาสนศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต มหาวิทยาลัยรามคำแหง. สืบค้น 4 เมษายน 2567, จาก http://www3.ru.ac.th/mpa-abstract/index.php/abstractData/viewIndex/378
Ahmad, S. (2017). Work Stress and Employee Performance. ZENITH International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research,7(11), 48-57.
Bloom, B. S., Madaus, G. F., & Hastings, J. T. (1971). Handbook on Formative and Summative Evaluation of Student Learning. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Dondi, M., Klier, J., Panier, F., & Schubert, J. (2021). Defining the skills citizens will need in the future world of work. McKinsey & Company, 25, 1-19.
Harvard University. (2020). 21st Century Learning. Retrieved March 24, 2023, from http://exploresel.gse.harvard.edu/frameworks/3
Kleiman, L. (2018). Getting Control of the VUCA World: Volatile, Uncertain, Ambiguous and Complex. Retrieved September 1, 2023, from https://www.hrtopics.com/blog/getting-control-of-the-vuca-world-volatile-uncertain-ambiguous-and-complex
Mckinsey & Company. (2022). Hybrid working models can leverage talent and skills across industries. Retrieved March 24, 2023, from https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/metals-and-mining/our-insights/hybrid-working-models-can-leverage-talent-and-skills-across-industries
Skills Future Singapore (2022). Skills Demand for the future economy. Retrieved April 17, 2023, from https://www.skillsfuture.gov.sg/docs/default-source/skills-report-2023/sdfe-2023.pdf
Stoilkovska, A., & Serafimovic, G. (2017). Job Analysis as an important human resources management function. International Refereed Scientific Journal Vision, 2(1), 113-124.
U.S. Department of Labor. (2023). Soft Skills: The Competitive Edge. Retrieved June 16, 2023, from https://www.dol.gov/agencies/odep/publications/fact-sheets/soft-skills-the-competitive-edge
UNESCO-UNEVOC International Centre. (2022). Digital competence frameworks for teachers, learners and citizens. Retrieved May 14, 2023, from https://unevoc.unesco.org/home/Digital+Competence+Frameworks
World Economic Forum. (2023). Future of Jobs Report 2023 Insight Report. Retrieved April 6, 2023, from https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Future_of_Jobs_2023.pdf
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Humanities and Social Sciences Journal of Pibulsongkram Rajabhat University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Any articles or comments appearing in the Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, Rajabhat Phibulsongkram University, are the intellectual property of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect the views of the editorial board. Published articles are copyrighted by the Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, Rajabhat Phibulsongkram University.








