การศึกษาปัจจัยตัวชี้วัดการพัฒนาพื้นที่โดยรอบสถานีขนส่งมวลชน ที่มีผลต่อคุณภาพเมือง: กรณีศึกษา โครงการรถไฟฟ้ารางเบาจังหวัดเชียงใหม่
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14456/psruhss.2024.24คำสำคัญ:
การพัฒนาพื้นที่โดยรอบสถานีขนส่งมวลชน , รถไฟฟ้ารางเบาจังหวัดเชียงใหม่ , การพัฒนาเมืองอย่างยั่งยืนบทคัดย่อ
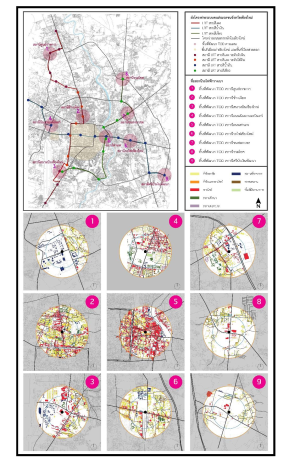
การขยายตัวของเมืองและเศรษฐกิจเชียงใหม่ในปัจจุบัน ส่งผลกระทบโดยตรงต่อคุณภาพเมืองอย่างเห็นได้ชัด อาทิ ปัญหาการจราจร และมลภาวะทางอากาศ ในความพยายามแก้ไขปัญหาข้างต้น จึงได้มีการศึกษาโครงการรถไฟฟ้ารางเบาจังหวัดเชียงใหม่ขึ้น ซึ่งได้มีการนำแนวคิดการพัฒนาพื้นที่โดยรอบสถานีขนส่งมวลชน (Transit-Oriented Development: TOD) มาใช้ประกอบการพัฒนาโครงการ เพื่อให้เมืองเชียงใหม่มีการเติบโตสอดคล้องกับการพัฒนาประเทศ โดยงานวิจัยนี้ มีวัตถุประสงค์ 2 ประเด็น คือ 1) เพื่อศึกษาตัวชี้วัดการพัฒนาพื้นที่โดยรอบสถานีขนส่งมวลชน (TOD Indicators) ภายใต้บริบทเมืองเชียงใหม่ จากการศึกษาและทบทวนวรรณกรรม และถอดบทเรียนจากแนวปฏิบัติที่ประสบความสำเร็จ 2) เพื่อสังเคราะห์ตัวชี้วัดการพัฒนาพื้นที่โดยรอบสถานีขนส่งมวลชนจังหวัดเชียงใหม่ ผ่านการสำรวจพื้นที่โดยรอบสถานีรถไฟฟ้ารางเบา จำนวน 9 พื้นที่ และสังเคราะห์ปัจจัยที่เหมาะสมสำหรับการพัฒนาคุณภาพเมือง ผลการศึกษาพบตัวชี้วัดการพัฒนาพื้นที่โดยรอบสถานีขนส่งมวลชน ภายใต้บริบทของเมืองเชียงใหม่ทั้งหมด 15 ตัวชี้วัด จาก 3 ด้าน จากแนวคิดการพัฒนาเมืองอย่างยั่งยืน (Urban Sustainable Development) คือ 1) ด้านสังคมและวัฒนธรรม 2) ด้านกายภาพและสิ่งแวดล้อม และ 3) ด้านเศรษฐกิจ ซึ่งเป็นข้อมูลสำหรับการพัฒนายุทธศาสตร์และวางผังพื้นที่อย่างเหมาะสมต่อไป
เอกสารอ้างอิง
การรถไฟฟ้าขนส่งมวลชนแห่งประเทศไทย (2562). รายงานความก้าวหน้าเดือนที่ 6 (Progress Report No.6) โครงการศึกษารายละเอียดความเหมาะสม ออกแบบเเละจัดเตรียมเอกสารประกวดราคา โครงการระบบขนส่งจังหวัดเชียงใหม่ สายสีเเดง (โรงพยาบาลนครพิงค์ - เเยกเเม่เหียะสมานสามัคคี). กรุงเทพฯ: การรถไฟฟ้าขนส่งมวลชนแห่งประเทศไทย (รฟม.).
พนิต ภู่จินดา, และยศพล บุญสม. (2559). แนวคิดการพัฒนาเมืองต้นแบบ. เจ-ดี : วารสารวิชาการ การออกแบบสภาพแวดล้อม, 3(1), 21-43.
มนสิชา เพชรานนท์. (2561). การวิเคราะห์ศักยภาพเชิงพื้นที่เพื่อการพัฒนา TOD เมืองขอนแก่น. วารสารสิ่งแวดล้อมสรรค์สร้างวินิจฉัย คณะสถาปัตยกรรมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยขอนแก่น, 17(2), 93-113.
อัมพิกา ชุมมัธยา, และณวิทย์ อ่องแสวงชัย. (2561). การขยายตัวของเมืองกับการเปลี่ยนแปลงบริบทของย่านเมืองเก่าในจังหวัดเชียงใหม่. เจ-ดี: วารสารวิชาการ การออกแบบสภาพแวดล้อม, 5(1), 61-81.
Bertolini, L. (1999). Spatial development patterns and public transport: The application of an analytical model in the Netherlands. Planning Practice and Research, 14(2), 199-210.
Calthorpe Associates. (1990). Transit-oriented development design guidelines. California : Author.
Center for Transit-Oriented Development. (2011). Transit-oriented development strategic plan for metro TOD program. Portland, Oregon.
Center for Transit-Oriented Development. (2013). Transit-oriented development typology strategy for Allegheny county. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
Chorus, P., & Bertolini, L. (2011). An application of the node place model to explore the spatial development dynamics of station areas in Tokyo. The Journal of Transport and Land Use, 4(1), 45-58.
Huang, R., Grigolon, A., Madureira, A. M., & Brussel, M. (2018). Measuring transit-oriented development (TOD) network complementarity based on TOD node typology. Journal of Transport and Land Use, 11(1), 304-324.
Ivan, I., Boruta, T., & Horak, J. (2012). Evaluation of railway surrounding areas: the case of Ostrava city. WIT Transactions on The Built Environment, 128, 141-152.
Kamruzzaman, M., Baker, D., Washington, S., & Turrell, G. (2014). Advance transit oriented development typology: case study in Brisbane, Australia. Journal of Transport Geography, 34, 54-70.
Li, Z., Han, Z., Xin, J., Luo, X., Su, S., & Weng, M. (2019). Transit oriented development among metro station areas in Shanghai, China: Variations, typology, optimization and implications for land use planning. Land Use Policy, 82, 269-282.
Liu, Y., Singleton, A., & Arribas-Bel, D. (2020). Considering context and dynamics: A classification of transit-orientated development for New York City. Journal of Transport Geography, 85, 102711.
Lyu, G., Bertolini, L., & Pfeffer, K. (2016). Developing a TOD typology for Beijing metro station areas. The Journal of Transport Geography 55, 40-50.
Monajem, S., & Nosratian, F. E. (2015). The evaluation of the spatial integration of station areas via the node place model; an application to subway station areas in Tehran. Transportation Research Part D, 40, 14-27.
Ratner, K. A., & Goetz, A. R. (2013). The reshaping of land use and urban form in Denver through transit-oriented development. Cities, 30, 31-46.
Shastry, S. (2010, August). Spatial assessment of transit oriented development in Ahmedabad, India (Master's thesis). Retrieved January 13, 2022 from: https://essay.utwente.nl/59707/
Singh, Y. J., Fard, P., Zuidgeest, M., Brussel, M., & Maarseveen, M. V. (2014). Measuring transit oriented development: a spatial multi criteria assessment approach for the City Region Arnhem and Nijmegen. Journal of Transport Geography, 35, 130-143.
Su, S., Zhang, H., Wang, M., Weng, M., & Kang, M. (2021). Transit-oriented development (TOD) typologies around metro station areas in urban China: A comparative analysis of five typical megacities for planning implications. Journal of Transport Geography, 90, 102939.
Taki, H. M., & Maatouk, M. M. (2018). Promoting transit oriented development typology in the transportation planning. Communications in Science and Technology, 3(2), 64-70.
Teklemariam, E. A., & Shen, Z. (2020). Determining transit nodes for potential transit-oriented development: Along the LRT corridor in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Frontier of Architectural Research, 9, 606-622.
United Nations. (2015). The 17 Goals. Retrieved September 15, 2020: https://sdgs.un.org/goals
Vale, D. S. (2015). Transit-oriented development, integration of land use and transport, and pedestrian accessibility: Combining node-place model with pedestrian shed ratio to evaluate and classify station areas in Lisbon. Journal of Transport Geography, 45, 70-80.
Zemp, S., Stauffacher, M., Lang, D. J., & Scholz, R. W. (2011). Classifying railway stations for strategic transport and land use planning: Context matters!. Journal of Transport Geography, 19, 670-679.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 วารสารมนุษยศาสตร์และสังคมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏพิบูลสงคราม

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความหรือข้อคิดเห็นใดใดที่ปรากฏในวารสารมนุษยศาสตร์และสังคมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏพิบูลสงครามเป็นวรรณกรรมของผู้เขียน ซึ่งบรรณาธิการไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารมนุษยศาสตร์และสังคมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏพิบูลสงคราม








